The official discord link if you wish to join the discord: https://discord.gg/j5RKwCvAFu
Support the wiki on our official Ko-Fi page or Patreon page!
Category:Female Characters: Difference between revisions
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Venus_symbol.png|center|400px]] | |||
An organism's sex is '''female''' (symbol: ♀) if it produces the large non-motile ovum (egg cell), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete (sperm cell) during sexual reproduction. | |||
The symbol of the Roman goddess Venus is used to represent the female sex in biology. It also stands for the planet Venus and is the alchemical symbol for copper. | |||
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and males are results of the anisogamous reproduction system, wherein gametes are of different sizes (unlike isogamy where they are the same size). The exact mechanism of female gamete evolution remains unknown. | |||
In species that have males and females, sex-determination may be based on either sex chromosomes, or environmental conditions. Most female mammals, including female humans, have two X chromosomes. Female characteristics vary between different species, with some species having pronounced secondary female sex characteristics, such as the presence of pronounced mammary glands in mammals. | |||
Latest revision as of 09:07, 1 February 2023
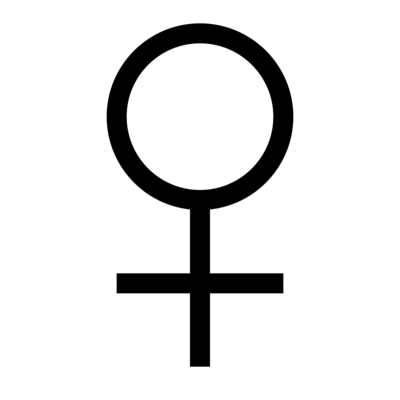
An organism's sex is female (symbol: ♀) if it produces the large non-motile ovum (egg cell), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete (sperm cell) during sexual reproduction.
The symbol of the Roman goddess Venus is used to represent the female sex in biology. It also stands for the planet Venus and is the alchemical symbol for copper. A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and males are results of the anisogamous reproduction system, wherein gametes are of different sizes (unlike isogamy where they are the same size). The exact mechanism of female gamete evolution remains unknown.
In species that have males and females, sex-determination may be based on either sex chromosomes, or environmental conditions. Most female mammals, including female humans, have two X chromosomes. Female characteristics vary between different species, with some species having pronounced secondary female sex characteristics, such as the presence of pronounced mammary glands in mammals.
Pages in category "Female Characters"
The following 200 pages are in this category, out of 478 total.
(previous page) (next page)A
- Adeleine & Ribbon
- Aerith Gainsborough
- Agathe (Beauty and the Beast)
- Agent 3 (Splatoon)
- Aki Jakago
- Aki Narukami
- Alia (Mega Man X)
- Alice (Bibliomania)
- Alice (Disney Infinity)
- Alice (Megami Tensei)
- Alli
- Alucard (Hellsing)
- Ami
- Amy Rose
- Amy Rose (Chronicles)
- Amy Sorel
- Ana
- Ana (The Child)
- Anabelle
- Android 18
- Ankha
- Anko Uguisu
- Anna (Disney Infinity)
- Anna (Frozen)
- Annalisa
- Anne Boonchuy
- Anne Frank (Goku × Anne Frank: Until the End of Time)
- Apogee
- Ariel
- Ariel (NES)
- Ariel (Sega Genesis)
- Ashi
- Ashley Graves
- Audrey Fremont
- Aurora (Disney)
- Ava
- Ava Ire
- Aya Drevis
- Ayla
B
C
- Carmen Sandiego (2019)
- Carrie White (1976 Movie)
- Carrie White (2002 Movie)
- Carrie White (2013 Movie)
- Cassandra (Pico's School)
- Cassandra Alexandra
- Catherine
- Caulifla
- Cerberus (Helltaker)
- Cere Junda
- Chantel DuBois
- Charlise
- Chronoa
- Chronoa (Dragon Ball Heroes)
- Chun-Li
- Churra
- Cinderella
- Circus Baby
- Cissnei
- Colette (Disney Heroes: Battle Mode)
- Crisbell
- Curly Brace
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
- Kafka
- Katie Clay
- Katt
- Kei Sagami
- Kick-Ass (2018)
- Kid (Chrono Cross)
- Kid (Radical Dreamers)
- Kijimuna (Doodle Champion Island)
- Kiki
- Kiki (The Child)
- Kikoru Shinomiya
- Kilala Reno
- King Knight
- Kitty
- Knight (Candies n' Curses)
- Knives Chau (Video Game)
- Komodo Dragon
- Korsica
- Kouko Ishigami
- Kronika
- Krystal
- Kyuu
